Cancer Treatment

Overview
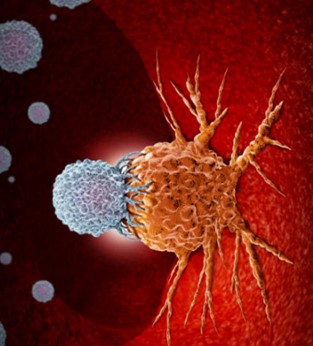
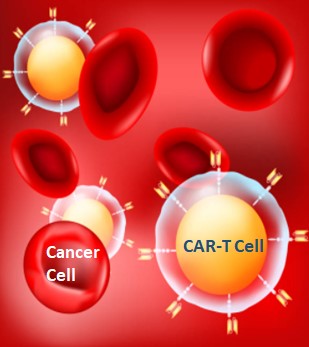
The goal of cancer treatment is to achieve a cure for cancer patients, allowing them to live a normal life span. It may or may not, depending on their specific situation, If a cure isn't possible, their treatments may be used to shrink their cancer or slow the growth of their cancer to allow them to live symptom free for as long as possible. In addition to the three major methods of cancer treatment, namely surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy, targeted therapy is in the ascendant and due to the understanding of the physiology and molecular mechanism of cancer cells, small molecule therapies have sprung up like mushrooms, including CAR T-cell immunotherapy treatment brings new hope to this ultimate goal.
Cancer Treatment Plan
Treating cancer can involve a number of different specialists, medical practices, and caregivers. It’s important that every person involved in the process fully understands the patient’s cancer, treatments, symptoms, and goals. That is why SERO recommends all our patients maintain an updated cancer treatment plan. A written cancer treatment plan outlines all aspects of a patient’s cancer and treatments. This ensures every provider and caretaker understands the patient’s history and goals and can provide treatment accordingly. When you are diagnosed with cancer, your first step is to choose your treatment options. Doing so may involve the opinions of multiple specialists, friends, and loved ones. Once you decide on a treatment or treatments, you and your doctors will plan and schedule them. These planning and scheduling decisions make up your treatment plan.For cancer treatment plan details..(Read More>) // Download the reference of cancer treatment plan document(Download>)
Three cancer treatment methods
There are three cancer treatment methods as below
1.Primary treatment:
The goal of a primary treatment is to completely remove the cancer from your body or kill all the cancer cells. Any cancer treatment can be used as a primary treatment, but surgery is the most common primary cancer treatment for the most common types of cancer.
2.Adjuvant treatment:
The goal of adjuvant therapy is to kill any cancer cells that may remain after primary treatment in order to reduce the chance that the cancer will recur. Any cancer treatment can be used as an adjuvant therapy. Common adjuvant therapies
 include chemotherapy, radiation therapy and hormone therapy.
include chemotherapy, radiation therapy and hormone therapy.
3.Palliative treatment:
Palliative treatments may help relieve side effects of treatment or signs and symptoms caused by cancer itself. Surgery, radiation, chemotherapy and hormone therapy can all be used to relieve symptoms. Other medications may relieve symptoms such as pain and shortness of breath.

AI in Cancer Treatment
Despite major advances in treatment over the past decades, cancer remains one of the most deadly diseases worldwide. Early detection and care are the best tools doctors have against the disease. However, challenges including high false-positive rates and difficult predicting treatment success can slow down the process. Healthcare professionals are finding ways to apply the latest developments artificial intelligence AI to the treatment of cancers. There are five of these innovative technologies:1) Improving lung cancer screening
Lung cancer screening with the use of computed tomography (CT) is highly effective in reducing the mortality rate of lung cancer.
2) Ruling out false positives and negatives
 AI-boosted detection methods may result in quicker treatment for the patients that need it, while sparing those who may have been incorrectly considered at high risk for cancer with previous diagnostic methods.
AI-boosted detection methods may result in quicker treatment for the patients that need it, while sparing those who may have been incorrectly considered at high risk for cancer with previous diagnostic methods.3) Predicting immunotherapy success
Immunotherapy is a relatively new treatment for cancer that uses drugs to boost the human immune system and help it fight off malignant cells. New AI tool combinated with regular CT scans, an algorithm could be used to identify patients who are most likely to respond well to immunotherapy
4) Improving radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is one of the most effective treatments available for many different types of cancer. However, it is extremely hard on the body, and it is often difficult to predict how patients will react. AI artificial intelligence was successfully used to help doctors plan where to target radiation therapy and forecast how well a patient is likely to hold up to the effects.
5) Personalized cancer treatment
The AI model used by the clinic works with a combination of medical records and patient health history, along with CT scans. It builds customized programs for each patient based on a mathematical model that estimates how well they would respond to certain treatments.

Precision medicine
Precision medicine called personalized medicine or personalized care is a way to offer and plan specific care for patients, based on the paatient's genes (or the genes in cancer cells). Precision medicine looks at how a specific gene mutation might affect a person's risk of getting a certain cancer or, if already have cancer, how genes (or genes in their cancer cells) might affect treatment.Gene mutations
Each cell in a patient's body has DNA which contains genes. Genes are the instruction cells use to make proteins needed to keep body working normally. When cells divide to make new cells, the genes inside those cells are copied. A gene change happens when there's a mistake in the copying process. Sometimes these changes come from a parent. But they can also happen sometime later in life for gene changes. Some gene changes can be harmful, while others may not cause any problems.
But they can also happen sometime later in life for gene changes. Some gene changes can be harmful, while others may not cause any problems.Gene mutation caused cancer
All cancers are caused by a genetic change or mutation of some kind. Cancer cells are mutated versions of normal cells, meaning something changed in a normal cell to make it turn into a cancer cell.While we don't yet know all the genes and mutations that could be involved in the development of cancer, there are some we know about and can test for. Depending on the type of mutation, an abnormal gene change might make a person more likely to develop a certain cancer.and if they already have cancer, the abnormal gene might mean that the cancer may not respond well to a certain type of treatment or drug. In some paient with cancer, a specific gene mutation might mean that their prognosis outcome is better or worse than someone with the same cancer who does not have that gene change.

Gene diagnosis and treatment
Patient with a cancer diagnosis, their tumor might be tested for certain types of gene changes or proteins made from those gene changes. This testing can provide information about how their cancer grows and spreads. It also called biomarker tests (chromosome tests, gene tests, or biochemical tests) It might be done using a blood or saliva sample, biopsy tissue, or body fluids.In some cancers, the gene testing done on a tumor can affect treatment choices. This is because certain gene changes can affect how a tumor responds to certain treatments and some tumors have gene changes that are different from other tumors of the same type. For treatment, the major goal is to give a target gene mutation treatment, without causing too many side effects, and to avoid giving treatments that might not work.
Types of cancer where precision medicine is used
It's important that precision medicine is not used for every cancer. Treatments will be customized to the specific gene changes in each patient’s cancer. Some of the more common cancers where precision medicine is being used to help with treatment decisions including Colorectal cancer, Breast cancer, Lung cancer, Certain types of leukemia, Certain types of lymphoma, Melanoma, Esophageal cancer, Stomach cancer, Ovarian cancer, and Thyroid cancer.
Biomarker test
There are many types of cancer treatment, The types of treatment that one receives will depend on the type of cancer one has and how advanced it is. Some people with cancer will have only one treatment. But most people have a combination of treatments. When one need treatment for cancer, one has a lot to learn and think about. It is normal to feel overwhelmed and confused. But, talking with doctor and learning about the types of treatment for more control.Before to do cancer treatment, there is an important testing from doctor called Biomarker testing which is a way to look for genes, proteins, and other substances(called biomarkers or tumor markers) that can provide information about cancer. It can help doctor choose the best cancer treatment for patient. Please get more detail information form below Biomarker testing and cancer treatment types.
Cancer treatment types
The most important cancer treatment types are immunotherapy, CAR-T, bone marrow (Stem cell) transplant, surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, targeted therapy, cryoablation, radiofrequency ablation, hyperthermia, photodynamic therapy and clinical trials.

 EN
EN